Shape Levels of Perspective & Informations Processes
Down, we have the “basic level” and up to “general level.” On the right side, we have “decision taken with good information” and, on the left side, “decisions not made according good information.” There is flexibility in definitions like what is good or bad information. The graph just expresses a critical transition. That is to say, when and with what, being satisfied with the information process (forward–left) and not (backward–right).
We suppose that sustainability is made of good social decisions. The problem is with how to have “good” knowledge and what to do, and we often have to presume that everyone is positive in this sense and plays fair. This is not necessarily normal. Information is also relative, the same way good decisions in complex situations cannot be perfect, the same way we understand that an emergency has not enough time to decide with all information that make good decisions. Directly, within problems, some of our practices will be tainted by “localism,” the defect not to measure social scale or all range of the phenomena and and at a level improper to the best solution. Equipment will arrive too late and affected people will not care more for the community. At the same time, it is not very common to have dictators making their decisions only with perfect “centralism,” that is without good information and only bad decisions. Their regime would not remain for long. So they have to know effective things or have special extraordinary resources.
*At a basic level, there is “direct processes of information” with ground level of technical studies. At a higher level, we often have to consider with complexity, where collaborative cautious world driven by principles of precautions that may prevail over norms, philosophy, and models. This kind of information must have perspectives. Over the middle horizontal axis of separation, transitions are the mechanisms used to generalize or bring up decisions (for beefed down effects). From the left, down to up side, you meet “administration,” which links local to central. On the left upside with bad information, decisions will probably be based on authoritarian centralist mechanisms if only taken at that place. But, in emergencies, this can nevertheless work because of experience of trusted actors (or leaders) over basic level of social trustworthy actors, thus authorities not so dictatorially blind.
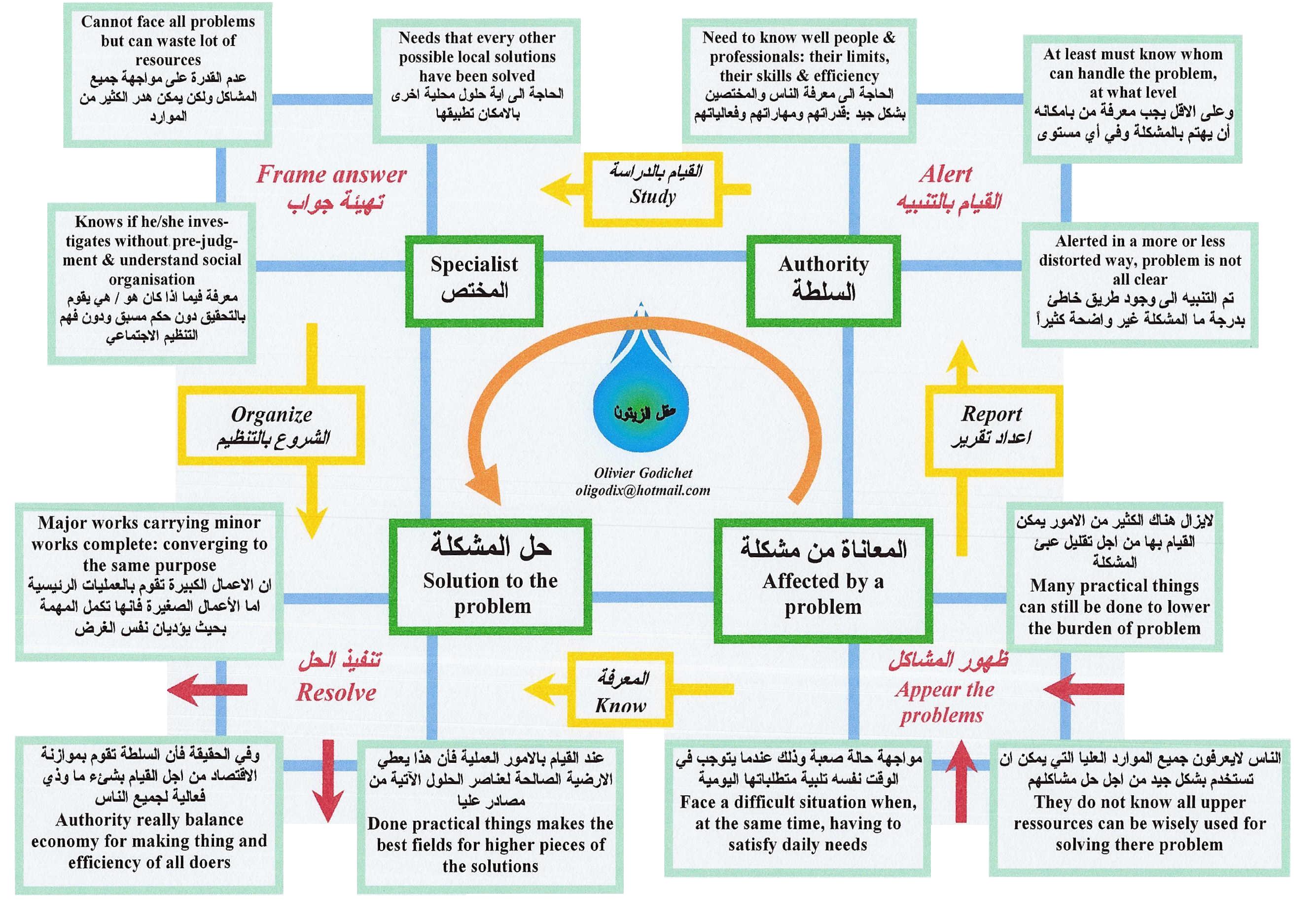
A proper management process would be to ask for studies of perspective of when having proper mechanisms of collection of information. So, to boserve a transition of position to decide from a not well informed higher level (left upside) to a well informed position (right upside). In the hope that weel informed decisions will be done with a sense of democratic priorities and feasible. Thereafter, it is expected that the technical apparatus of the state (“technocracy”) would be willing to have some positive contribution in the process of organization from a global and well-informed level of “rationality.” This also is about knowing what to do and what to save. Practically to have models of intervention, training, and reasoning from past experience and sort of good translations to put them into operations and good practices , so as to cope wisely with “reality” and land on practical issues.
A real complex process combines time, space, and persons between different levels of practice. The reader must intuitively understand that basic programmed things must be mainly composed of “reality” (as written in the scheme down and on the left side). The criteria to judge decisions on abstract or theoretical levels will especially consider technical criteria and operative priorities; meanwhile, criteria are often ethical and cultural. To land on what could be called reality’s rationality, will need modesty (a rational frame is not a truth, just a means) and organization. Even if we do not know how to define reality precisely, making that liability become a basic criteria recognized by people. We differentiate between passive and active extreme attitudes. It is not always justified to interfere in social processes and said leaders in charge can often let things follow their own process or answer only at one part or period of it. Anyway, make it clear in the chart the reason to allow local initiatives. Traditionally, what is higher is more for strategic things.
Ideal concern will consist of seeking the future when the community has the capacity, without wasting time to solve its problems. Now, also, this basic cell structure can consider, like the bricks of a wall, that there are more levels of integration as there are levels of government or means of intervention (say equipment for civil engineering). Of course, articulation, coordination, proper information, links of reports, and communication have to be defined.