Sorts of Mistakes
The study of types of mistakes have the purpose to check, suspect and identify technically the sort of mistakes, anyone makes and tries to correct. In a complex world, anyone makes mistakes. One would say that the difference between people are more in the skills developed to detect them soon, correct and not dissimulate.
Triangle of the olicognograph disposes the most common types of mistakes as paradoxes, fallacies and bias. They look like technical terms but sometimes it is necessary to understand the concept and derive analogies without rigidities, dogmatism and/or too rigid paradigm since it is not to pretend to never make mistake but to prevent most important inconvenients are faced and reduced as soon as possible. In the same way observe that simplifications, divisions and paradigms have often the aim to control excess of mistakes and reduce difficulties created by uncertainties.
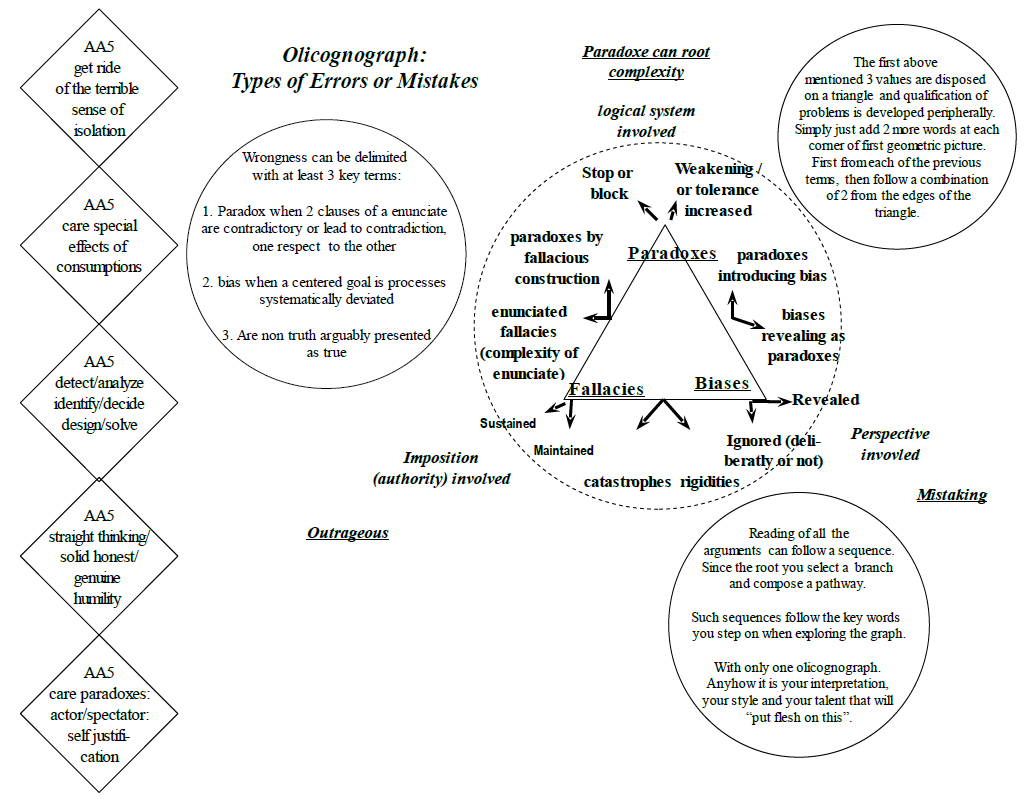
Paradox can be seen as true enunciate containing a logical impossibility (more often respect to the enunciate rather than against reality (which is in fact and necessarily in our opinion full of paradoxes). In common popular say: "the exception that confirm the rule". The point with paradox is to identify formal logical tools for what their are and not for unnecessarily locking everything of reality. Meanwhile plenty of paradoxes can be just mistakes of proper enunciates. It is not showing incapacity in producing good enunciates that you also show your logical capacity.
Bias could be understood with the picture of a target when systematically pointing not all and mainly at the middle, but on less than all 4 sectors (between 3 and 0, being the zero that you do not hit at any part of the target). Thus you may have some different patterns of bias, or use another picture than round target like: up and down and so on.
Fallacy could be seen as an assertion obviously false, like compared to neutral and advised opinion but imposed, maintained and sustained, up to absurdity by someone that may have authority but more often power to maintain it despite evidence. In complex reality it is also sometimes not so easy, the obvious may also be itself a fallacy. An injustice is often fallacious.
Then none of these types of mistakes are exclusive and they can be combined, 2 by 2 at first thus the sort of detail we give.